






Atopic dermatitis in dogs is a chronic inflammatory skin condition caused by an overactive immune response to environmental allergens. This condition, also known as canine atopy, results in persistent itching, redness, and irritation, significantly impacting a dog’s quality of life. Dogs suffering from atopic dermatitis often exhibit excessive scratching, licking, and skin infections, making early diagnosis and proper treatment essential for long-term relief.

Dogs with atopic dermatitis react to allergens that are typically harmless to most pets. These allergens trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation and intense itching. The most common allergens include:
Dogs with seasonal allergies often experience worsening symptoms during specific times of the year, while others suffer from year-round irritation due to indoor allergens.
Although food allergies are not a direct cause of atopic dermatitis, they can worsen symptoms. Common food allergens include:
Dogs with food allergies may exhibit chronic ear infections, digestive issues, and inflamed skin, making it essential to assess diet as part of the treatment plan.
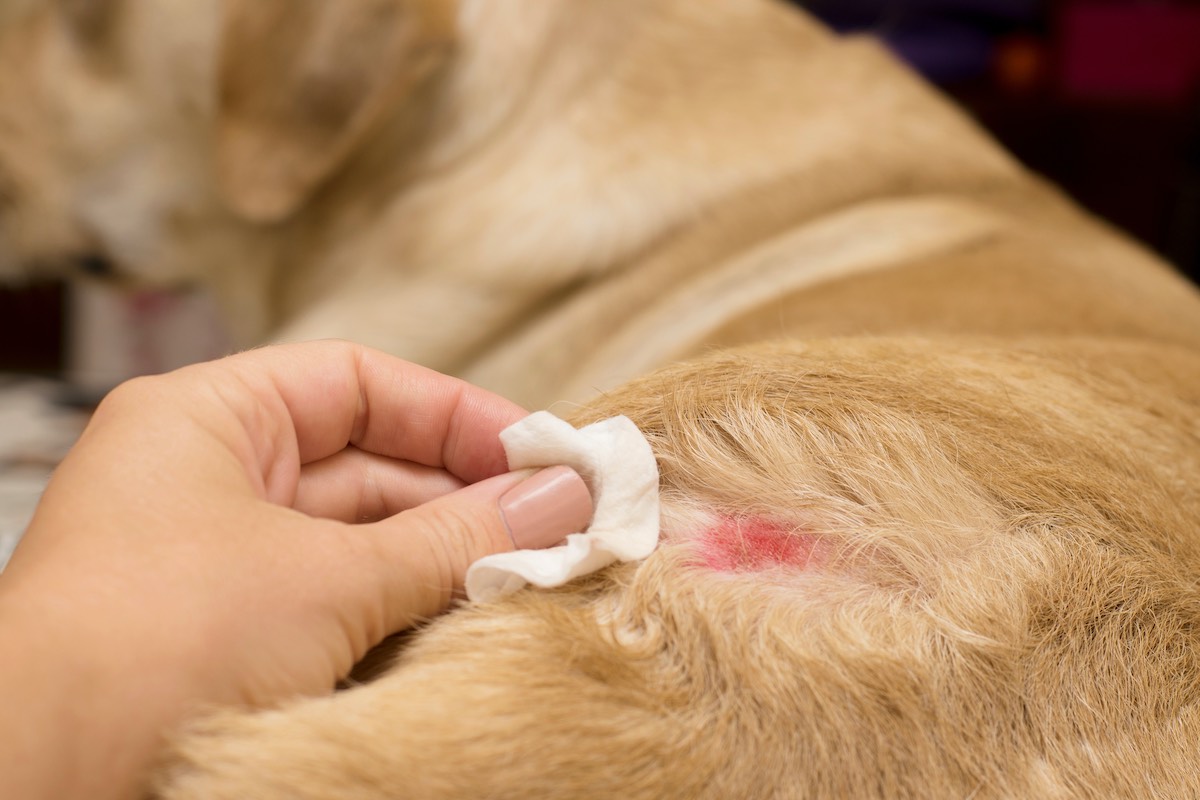
Even a single flea bite can trigger an extreme allergic reaction in some dogs. Flea saliva causes intense itching and inflammation, often leading to hot spots, scabs, and secondary skin infections. Regular flea prevention is crucial for dogs prone to atopic dermatitis.
Certain breeds are more susceptible to atopic dermatitis due to inherited traits. Breeds with a higher likelihood of developing canine atopic dermatitis include:
If a dog has a family history of skin allergies, it is more likely to develop atopic dermatitis at a young age.
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis vary in severity, but common signs include:
Atopic dermatitis typically worsens over time, making early intervention critical to prevent secondary infections and severe skin damage.
Veterinarians use a combination of clinical examination, allergy testing, and elimination trials to diagnose atopic dermatitis. Diagnostic methods include:
Proper diagnosis is essential to develop a targeted treatment plan tailored to the individual dog’s needs.
Effective management of canine atopic dermatitis involves a combination of medication, diet adjustments, environmental control, and long-term skincare.
Veterinarians often prescribe anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive medications to manage flare-ups, including:
Minimizing exposure to allergens can significantly reduce symptoms. Steps to control environmental allergens include:
A hypoallergenic diet can help manage atopic dermatitis in dogs, especially if food sensitivities contribute to symptoms. Consider the following dietary changes:
Allergy immunotherapy is a long-term treatment that helps desensitize a dog’s immune system to allergens. It involves customized allergy injections based on the specific allergens affecting the dog. This method has a high success rate in reducing atopic dermatitis symptoms over time.
Read Also :- Common Labrador Retriever Health Issues and How to Prevent Them
Common Health Issues in Siamese Cats and How to Prevent Them
While atopic dermatitis cannot always be prevented, proactive steps can reduce the risk and severity of flare-ups:
By managing triggers, diet, and skin health, dog owners can significantly improve their pet’s comfort and quality of life.
Atopic dermatitis in dogs is a complex condition that requires long-term management through proper diagnosis, allergen avoidance, medication, and specialized skincare. With the right approach, pet owners can help their dogs live a comfortable, itch-free life. Consulting a veterinarian for a customized treatment plan is the best way to manage atopic dermatitis effectively.
A combination of medications, diet changes, allergy shots, and skincare is the most effective treatment.
No, it is a chronic condition, but proper management can control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Persistent itching, red skin, ear infections, and excessive licking are common signs. A vet can confirm the diagnosis.
Dogs may need to avoid beef, chicken, dairy, wheat, soy, and artificial additives.
Oatmeal baths, coconut oil, and hypoallergenic diets can provide relief, but veterinary care is essential for severe cases.




